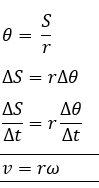What is circular motion?
Circular motion is a type of 2d motion. Circular motion describes the movement of an object that follows circular path. Circular motion can either be uniform or non-uniform.
Example: Rotation of earth around sun, rotation of
moon around earth, spinning of fan, wheel of automobile, etc.
In uniform circular motion the speed of body is
constant or fixed, whereas, in non-uniform circular motion the speed of body
vary at every point.
But there is an acceleration due to change in
direction at every point.
Circular motion follows angular variables due to
change of angle.
Read more: Projectile motion
Angular Quantities
Angular Displacement:
Angular displacement is angle at which body is
displaced. It is represented by θ.
Suppose a body moves from point p1 to p2 and covers a distance at circumference
of circle so the angle between two points will be angular displacement.
The S.I unit of angular displacement is radian.
One radian is defined as arc length equal to radius of circle.
One radian is equals to 57.3 degrees.
Angular Velocity:
The rate of change of angular displacement of body in
a circular motion is called angular velocity. It is represented by ω.
The S.I unit of angular velocity is 1 radian per
second.
The instantaneous angular speed is defined as limit of
this ratio as t approaches zero:
This equation gives magnitude of instantaneous angular
velocity.
Relation between angular and linear velocity
In this equation we have both linear and angular
velocity. We can summarize the equation that linear velocity is directly
proportional to angular velocity.
Angular acceleration:
The rate of change of angular velocity of body in
circular motion is called angular acceleration. It is represented by α.
Let ω1 and ω2
be the magnitude of angular velocities at time t1
and t2 so we will define average angular acceleration as:
The S.I unit of angular acceleration is radian per
second square.
As rate of rotation increases then angular acceleration
vector is parallel to angular velocity vector and if rate of rotation decreases
then the two vectors will be opposite.
Read more : Centripetal Acceleration
Relation between angular acceleration and linear acceleration
Tangential Velocity
Tangential velocity is velocity tangent to the circle.
The velocity produced on arc or tangent of circle is termed
as tangential velocity.
Tangential velocity is also called as linear velocity.
Tangential velocity of particle moving in a circular
path is given by the product of position vector r and angular velocity of
particle.
Note that:
Angular velocity of rotating body is same at every
point,
Whereas Tangential velocity is not same for every
point as at every point the tangent will be changed.
Si unit of tangential velocity is radian mater per
second
Tangential Acceleration
The rate of change of tangential velocity or linear
velocity is called angular acceleration.